
Read, Write or Create Data 46. These sample questions are simple and basic questions that represent likeness to the real IBM C2090-011 exam questions.Random Sampling 27. This sample practice exam gives you the feeling of reality and is a clue to the questions asked in the actual IBM Certified Specialist - SPSS Statistics Level 1 v2 certification exam.
Working with Many Files 22. Ranking, largest values, sorting, grouping 29. Test if file or variable exists 2.
Example, if youve ended up with categories with very few observations in them. An Ordinal variable is one where it is possible to rank the categories or put them in an order. In general, it is more reliable to use numeric codes to represent ordinal data. ROC curves 1.A codebook is a document containing information about each of the variables in your dataset, such as:For example, for a string variable with the values of low, medium, high, the order of the categories is interpreted as high, low,medium which is not the correct order.
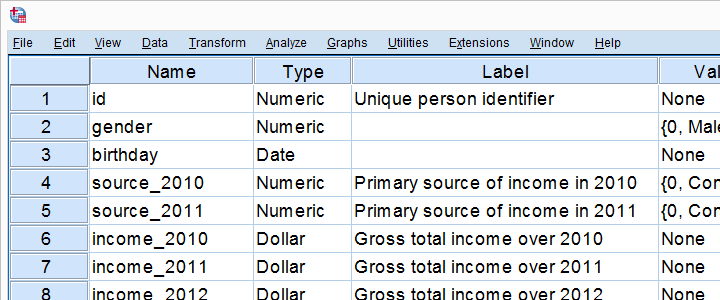
It also prints a table with the assigned value labels for categorical variables.You can generate this simple codebook using the point-and-click menus, or using syntax. It gives the names, labels, measurement levels, widths, formats, and any assigned missing values labels for every variable in the dataset. A good codebook allows you to communicate your research data to others clearly and succinctly, and ensures that the data is understood and interpreted properly.Many codebooks are created manually however, in SPSS, it's possible to generate a codebook from an existing SPSS data file.If you are not familiar with variable properties (such as labels or measurement levels) or concepts like value labeling of category codes in SPSS, you should read the Defining Variables tutorial before continuing.This codebook method prints most of the information found in the Variable View window. For categorical variables: If coded numerically, the numeric codes and what they representCodebooks can also contain documentation about when and how the data was created. For scale variables: The variable's units of measurement Numeric, string how many characters wide it is how many decimal places it has)
If you are using an older version of SPSS, this command is not available - it will not appear in the menus, and running the syntax will return error messages. Also unlike the simple method, the summary information for each variable will be printed in its own table.You can generate this detailed codebook using the Codebooks dialog window, or using syntax.Note: This procedure was introduced in SPSS version 17 ( source: SPSS v23 Command Syntax Reference). Unlike the simple method, you can choose which variables are included in the codebook, and you can choose which variable properties are included in the summary. Detailed codebookThis codebook method includes all of the same information as the simple method, but also includes options for printing summary statistics as well. The codebook will print to the Output Viewer window.Using Syntax DISPLAY DICTIONARY.
File information: None included by default. Variable information: By default, includes Position, Label, Type, Format, Measurement level, Role, Value labels, Missing values, and Custom attributes. In the Output tab: (Optional) Choose what variable and datafile properties you want to be included in the codebook: To include all variables, click inside the Variables box, press Ctrl + A, then click the arrow button. In the Variables tab: Add the variables you want in the codebook to the Codebook Variables box.
Spss Code Example Download The Sample
Run the syntax file on the sample data. By default, counts and percents will be printed for nominal and ordinal variables, and mean, standard deviation, and quartiles will be printed for scale variables./VARINFO POSITION LABEL TYPE FORMAT MEASURE ROLE VALUELABELS MISSING ATTRIBUTES/OPTIONS VARORDER=VARLIST SORT=ASCENDING MAXCATS=200/STATISTICS COUNT PERCENT MEAN STDDEV QUARTILES.Note: When listing the variable names in the syntax, the assigned measurement level must be given in brackets after each variable name: for scale, for nominal, for ordinal.To reproduce this example, download the sample SPSS dataset and SPSS syntax file. In the Statistics tab: (Optional) Choose what statistics you want in the codebook. Maximum number of categories: By default, limits to 200 categories. Can also order alphabetically, by file, or by measurement level.
This table summarizes variable-level information, including: TablesThe first table is the Variable Information table. Output Syntax DISPLAY DICTIONARY. Running the ProcedureTo generate a simple codebook for the sample data, click File > Display Data File Information > Working File. This includes having succinct but descriptive labels for your variables, and labels for any numeric codes used for categories.If you receive a dataset from a collaborator, you can get an overview of its contents by running the Display Dictionary procedure. Problem StatementWhen sharing your data with others, it's important that your variables are properly documented.
This table prints the name of each variable with defined value labels, and lists each code and associated label for that variable.Qualtrics users: This procedure works well with survey data that you've downloaded from Qualtrics in SPSS format. This table will only appear if you have value labels defined for at least one variable in your dataset otherwise, it is omitted. Measurement level (nominal, ordinal, scale)The second table is the Variable Values table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
